
FAQ
1. What are the most important criteria for selecting fiber optic cables?
Important selection and design considerations for fibre optic cabling:
- Link length
- Application
- Future performance
- Power budget
- Environmental requirements
2. Where are fiber optic cables typically used in the building?
Premises and enterprise networks (also called local area networks LAN) consist of four primary sections in which fibre optic cables can be installed from a communications pathway perspective: backbone/campus, data centre, riser and horizontal/desk.

| Section | Description | Cable type fibre |
| Backbone (Campus) | The backbone is typically the longest run in a premises network, often interbuilding. | OS2 |
| Data Centre | The data centre is a facility dedicated to data-intensive applications, where racks of interconnected equipment manage large amounts of information. | OS2, OM4, OM5 |
| Riser | The riser joins together equipment in a floor-level telecommunications closet and upper floor closets or zones. | OS2, OM3, OM4 |
| Horizontal (Desk) | The horizontal serves the desk or application workspace | OM3, OM4 |
3. What types of fiber optic cables are there and what are the differences?
The two major classifications of optical fibre cables are single-mode and multimode.
SINGLE-MODE FIBRES
Single-mode fibres are best suited for longer distance applications (>1 km). Single-mode fibre is designed to carry only one mode of light, and thus does not experience modal dispersion like multimode fibre.
Applications: LAN backbone, data centre, city network, access network, FTTx network, long haul network (WAN).
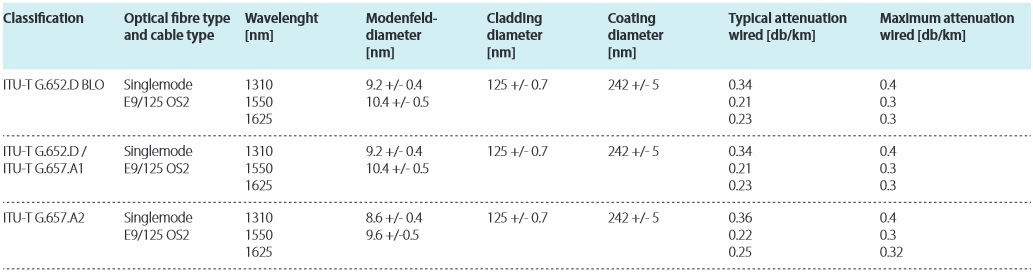
Optical single-mode fibre cable transmission performance parameters
The fibre designation (OS2) corresponds to the designation of ISO/IEC 11801 or EN 50173. OS2 is commonly referred to as
“low water peak” single-mode fibre and is characterized by having a low attenuation coefficient in the vicinity of 1383 nm.
MULTIMODE FIBRES
Multimode fibres are suitable for premises applications where the links are a few hundred meters long and there are many connectors. The larger core diameter of multimode fibre allows the use of affordable 850 nm transmittor diodes as well as low-cost connectors. Multimode fibre uses a graded index profile to minimize modal dispersion. This design maximizes bandwidth while maintaining large cores for simplified system assembly and lower network costs. For multimode fibres, bandwidth is the major limiting factor in network design.
Applications: in Premises cabling for LAN backbones (Campus and Vertical/Riser cabling), Fibre to the Office and Fibre to the Desk (FTTO, FTTD = horizontal cabling) as well as in Data Centre cabling.
Optical multimode fibre cable transmission performance parameters
The fibre designation (OM3 up to OM5) corresponds to the designation of ISO/IEC 11801 or EN 50173. Laser-optimised fibres are defined by their Effective Modal Bandwidth (minEMB, 850 nm VCSEL laser).

4. What fiber optic cables does SSB-Electronic GmbH offer?
At SSB-Electronic, you can purchase both universal fiber optic cables for indoor and outdoor applications, as well as fiber optic cables with special approvals, such as DNV approval for maritime application or fiber optic cables for installations in buildings with very high fire protection requirements (according to EN 50575).
Powered by Froala Editor
Powered by Froala Editor
